- What is a Shoulder Labral Tear?
- Common Causes of Shoulder Labral Tears
- Recognizing Symptoms of a Shoulder Labral Tear
- Diagnosing a Shoulder Labral Tear
- Treatment Options for Shoulder Labral Tears
- Recovery After Shoulder Labral Tear Treatment
- Why Choose Sano Specialty Care for Shoulder Labral Tear Treatment?
Are you experiencing persistent shoulder pain or feelings of instability? If so, you may be dealing with a shoulder labral tear. The labrum is a rubbery ring that surrounds the shoulder socket. Damage to the shoulder labrum is more common than you might think.
At Sano Specialty Care, our orthopedic specialists treat patients with pain and popping from labral tears. Whether you’re an athlete pushing your limits or dealing with everyday shoulder discomfort, learn about the causes of labral tears and how to regain your shoulder function and mobility.

What is a Shoulder Labral Tear?
The shoulder joint is a complex ball-and-socket mechanism. The labrum, a cartilage ring, helps stabilize the shoulder joint, keeping the "ball" securely in the "socket." A shoulder labral tear occurs when this cartilage ring is damaged or torn.
Common Causes of Shoulder Labral Tears
 Your shoulder joint is one of the most mobile—and vulnerable—joints in your body. The labrum, a ring of cartilage that stabilizes the joint, can tear due to sudden trauma, repetitive motion, or the natural aging process. Understanding the most common causes of labral tears can help you identify risk factors and seek early treatment before symptoms worsen.
Your shoulder joint is one of the most mobile—and vulnerable—joints in your body. The labrum, a ring of cartilage that stabilizes the joint, can tear due to sudden trauma, repetitive motion, or the natural aging process. Understanding the most common causes of labral tears can help you identify risk factors and seek early treatment before symptoms worsen.
Sports and Repetitive Overhead Motion
Athletes who engage in repetitive overhead movements, such as baseball pitchers, tennis players, and weightlifters, put significant strain on the shoulder joint. The constant stress on the labrum can lead to micro tears over time, gradually worsening until the cartilage is significantly damaged. Even non-athletes who frequently perform overhead motions—such as painters, construction workers, or fitness enthusiasts—can develop labral tears from repetitive use.
Interesting Fact: A study of 2,285 NFL players found that 14.9% showed MRI evidence of labral tears. Linebackers had the highest rate at 19.2%, while linemen were particularly prone to labral injuries in at least one shoulder.
Traumatic Injuries
A sudden impact or fall can cause a shoulder labral tear. Common traumatic events include:
- Falls on an outstretched arm – A hard landing can force the upper arm bone (humerus) into the socket, straining or tearing the labrum.
- Direct shoulder impact – Collisions in contact sports, car accidents, or workplace injuries can result in labral damage.
- Shoulder dislocations – When the ball of the joint pops out of the socket, the labrum often tears in the process.
Even one-time injuries can cause significant damage, particularly if left untreated.
Age-Related Wear and Tear
As we age, the cartilage in our joints naturally weakens. For individuals over 40, labral tears may develop gradually due to everyday use rather than a specific injury. This type of degeneration can lead to persistent shoulder pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion, often mistaken for general aging discomfort.
Heavy Lifting and Overuse
Lifting heavy objects with poor form or excessive strain on the shoulders—whether in the gym or during daily activities—can cause a labral tear. This is especially common among weightlifters who perform frequent bench presses, overhead presses, or pull-ups. The repetitive stress on the joint can lead to fraying or detachment of the labrum.
Recognizing Symptoms of a Shoulder Labral Tear
 Shoulder labral tears can be difficult to identify on your own, as their symptoms often mimic other common shoulder issues. However, persistent pain, instability, or mechanical sensations like clicking or popping may indicate a deeper issue within the joint. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a specialist for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Shoulder labral tears can be difficult to identify on your own, as their symptoms often mimic other common shoulder issues. However, persistent pain, instability, or mechanical sensations like clicking or popping may indicate a deeper issue within the joint. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a specialist for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
- Pain
A shoulder labral tear often causes persistent pain that can range from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing discomfort. Pain may worsen with specific activities, such as:- Reaching overhead (e.g., lifting objects, throwing a ball, or washing your hair).
- Extending your arm behind your back (e.g., putting on a jacket or reaching for a seatbelt).
- Lying on the affected shoulder, especially at night.
- Clicking, Popping, or Catching Sensations
Many individuals with labral tears report a popping, clicking, or catching feeling when moving their shoulder. This occurs because the torn labrum can interfere with the smooth motion of the joint, leading to mechanical symptoms. While occasional popping in the shoulder isn’t necessarily a concern, frequent or painful catching could indicate damage to the labrum. - Shoulder Instability or Weakness
The labrum plays a key role in keeping the ball of the shoulder joint securely in its socket. When torn, the joint may feel loose or unstable—especially during activities that require strength or rotation, such as lifting, pushing, or throwing. Some patients describe a sensation that their shoulder may “give out” or feel weak when carrying objects. - Reduced Range of Motion
A labral tear can lead to stiffness and restricted movement, making it difficult to fully extend, rotate, or lift your arm. Over time, avoiding certain movements due to discomfort can result in muscle imbalances and further limit mobility.
Diagnosing a Shoulder Labral Tear
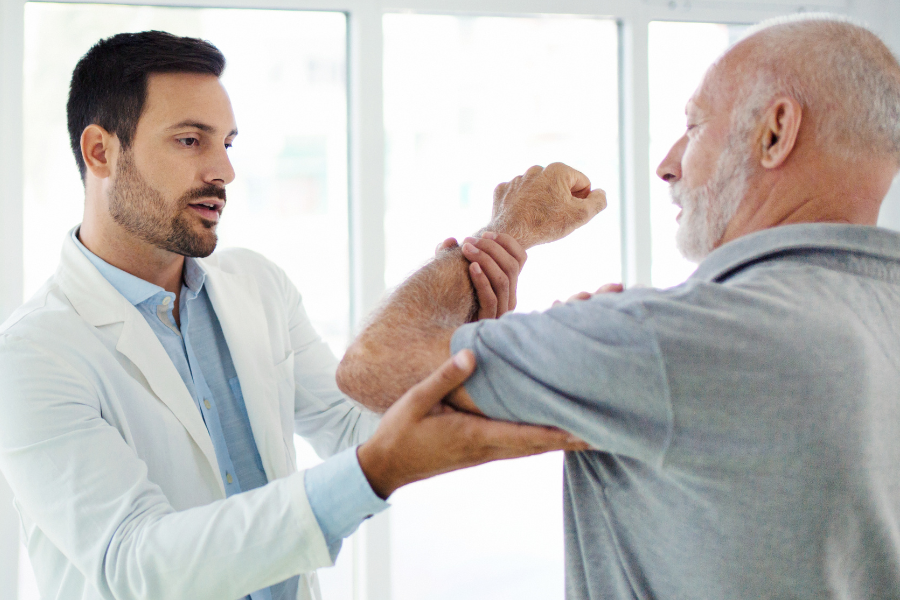 Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Sano Specialty Care's shoulder specialists use a combination of methods, including:
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Sano Specialty Care's shoulder specialists use a combination of methods, including:
Step 1: Medical History & Symptom Assessment
Your doctor will begin by discussing your medical history, symptoms, and activity level to better understand the nature of your shoulder pain. Key questions may include:
- When did the pain or discomfort begin?
- Did the symptoms start after a specific injury, or did they develop gradually?
- Have you experienced clicking, popping, or instability?
- What movements or activities make the pain worse?
This initial discussion helps narrow down potential causes and guide further testing.
Step 2: Physical Examination
A hands-on physical exam allows the specialist to evaluate:
- Range of motion – Testing how far and in what directions your shoulder can move.
- Strength testing – Assessing the function of surrounding musculature
- Pain triggers – Identifying movements or positions that cause discomfort.
- Instability signs – Checking if the joint feels loose or prone to dislocation.
During the exam, your provider may perform specialized orthopedic tests, such as the O’Brien test or the crank test, to stress the labrum and detect signs of tearing.
Step 3: Imaging Tests for Confirmation
If a labral tear is suspected, imaging tests help confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the damage:
- X-rays – While X-rays do not show soft tissue injuries, they help rule out fractures or arthritis that could contribute to shoulder pain.
- MRI or MRA (Magnetic Resonance Arthrography) – An MRI scan with contrast dye (MRA) provides the most detailed view of the labrum, highlighting tears and structural abnormalities.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography) – In some cases, a CT scan may be used to examine bone structure and joint alignment.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Labral Tears
The right treatment for a shoulder labral tear depends on the severity, location of the tear, and the patient’s activity level and lifestyle needs. Some labral tears heal well with conservative management, while others may require surgery to restore shoulder function and stability.
At Sano Specialty Care, our specialists take a personalized approach, ensuring each patient receives the most effective care for long-term recovery.
Non-Surgical Shoulder Treatments

For mild to moderate labral tears or those without significant instability, non-surgical treatments may effectively relieve pain and restore mobility.
- Rest & Activity Modification
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the shoulder, such as overhead motions or heavy lifting, can help prevent further damage.
- Temporary shoulder immobilization (such as using a sling) may be recommended in cases of acute injury.
- Medications
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications (such as ibuprofen or naproxen) help manage pain and swelling.
- In some cases, a corticosteroid injection may be recommended to reduce inflammation in the shoulder joint.
- Physical Therapy & Rehabilitation
- A structured physical therapy program can improve shoulder strength, flexibility, and stability, helping patients regain full function.
- Targeted exercises focus on:
- Strengthening the rotator cuff and shoulder stabilizing muscles.
- Improving joint mobility to reduce stiffness and pain.
- Enhancing posture and movement patterns to prevent re-injury.
Non-surgical treatments may be sufficient for patients with minor tears, particularly those who do not engage in high-impact activities.
Surgical Shoulder Treatments
For severe labral tears, persistent pain, or cases involving significant shoulder instability, surgical intervention may be the best option.
- Arthroscopic Labral Repair
- This minimally invasive procedure involves small incisions and the use of a small camera (arthroscope) to guide the surgeon.
- The damaged labrum is reattached to the shoulder socket using suture anchors, restoring joint stability.
- Labral Debridement (Removal of Damaged Tissue)
- In cases where the labral tear is small or repairable, the damaged portion may be trimmed away to prevent irritation and improve movement.
- Biceps Tenodesis (For SLAP Tears)
- If the tear involves the biceps tendon attachment (SLAP tear), the surgeon may release and reattach the tendon in a different location to reduce pain and restore function.
- Arthroscopic Labral Repair
- Latarjet Procedure
- In cases of severe shoulder instability, your surgeon may recommend an open procedure known as the latarjet procedure. This is typically recommended if arthroscopic intervention fails or the patient has severe bony deficiencies associated with recurrent dislocations.
Recovery After Shoulder Labral Tear Treatment
Whether you undergo surgical or non-surgical treatment, recovery is essential for regaining full shoulder function. Sano Specialty Care's shoulder specialists provide comprehensive rehabilitation programs, including:
- Physical Therapy: A customized exercise plan to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Activity Modification: Guidance on gradually returning to activities while protecting the shoulder.
- Dedicated return to throwing protocol for overhead athletes.
Why Choose Sano Specialty Care for Shoulder Labral Tear Treatment?
- Expert Shoulder Specialists: Our team of experienced orthopedic surgeons specializes in diagnosing and treating shoulder conditions.
- Comprehensive Care: We provide a full range of services, from diagnosis to rehabilitation.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: We tailor treatment to each patient's needs and goals.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Whenever possible, we utilize minimally invasive procedures to minimize pain and optimize recovery.
Don't let shoulder pain limit you. Contact Sano Specialty Care today to schedule a consultation with one of our shoulder specialists.